I started writing Fate’s Door at the beginning of January, thinking that it would be a novella, maybe 25,000 words long.
Fate’s Door tells the story of a sea nymph from the Middle Sea (the Mediterranean) who has taken a post as handmaiden to the three fates in the farthest north of Scandia (Scandinavia).
I envisioned my story telling of the heartbreaking dilemma she faces while fulfilling the duties of her post.
It’s her job to set out the materials the fates need for each day’s weaving. But on the terrible day that begins my story, she must set out the threads that will kill someone she loves very much, when the fates weave the threads into their tapestry fabric.
Must she do it? Or is there some way to subvert fate?
It turned out there was more to my story than I’d envisioned. A lot more! I’m closing toward the finish now, in July, but my word count is 115,000 words. Many more than the 25,000 I first thought would be enough. I expect to write another 30,000 words and complete the manuscript in early August.
My heroine has just finished crossing Európi (Europe) on horseback. In order to write about her journey, I did a lot of research about horses and, especially, horse gear.
In the 4th century BC, riders didn’t have the benefit of saddles or stirrups, but they did have the cushioning of a thick, felted blanket that was wrapped around the horse and secured snugly under its barrel.
Horseshoes were not invented until 500 AD, more than 800 years after my tale. But charioteers, cavalrymen, and traders were well aware that their horses needed hoof protection on paved roads and rough rocky ground. The hoof of a horse is made of keratin, the same stuff that composes hair and toenails. It wears down quickly on rough ground, and a horse without protection will quickly go lame.
So what did the ancients do?
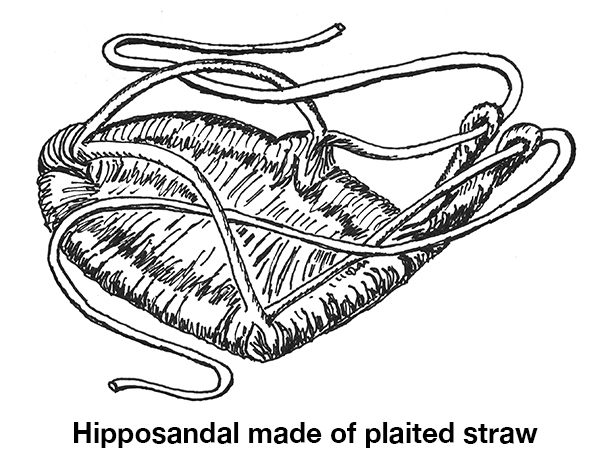
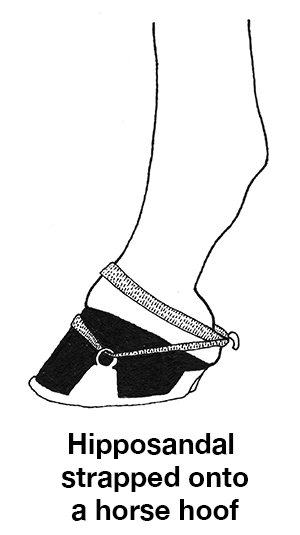
They devised the hipposandal. The earliest soles were made of plaited straw or broom and strapped onto the horse’s hooves. They could only be used once, and for a short time, before they wore out. The ancient Romans later termed them Soleae Sparteae, but my tale takes place when the ancient Greeks were the dominant culture in the Mediterranean, so I do not use the Roman term.
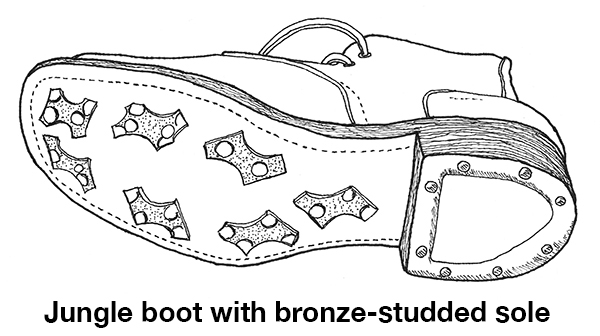
The horse “sandal” was improved to become a thick leather sole, studded with bronze cleats. The bronze cleats would protect the leather from wearing down so quickly and could be replaced when the bronze wore thin. The cleats presumably also gave better traction.
This is the form of horse sandal protecting the hooves of my heroine’s horse.
One source I read compared them to the jungle boots worn by US soldiers in World war II in places such as New Guinea, the Philipines, and Burma. I could not find any illustrations or diagrams of these leather and bronze horse sandals, but I did locate a photograph of the sole of a bronze-studded jungle boot, which I used to make a drawing of same. The horse sandal would, of course be shaped to fit a horse hoof, not a human foot, but I think you get the idea.
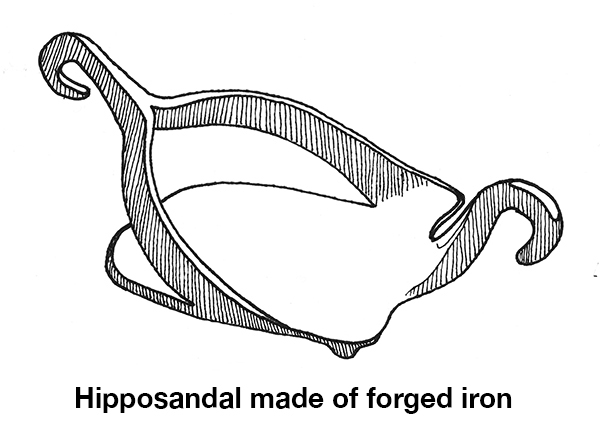
The ancient Romans made more improvements, creating the official hipposandal or Soleae Ferreae made of forged iron, but still attached to the hoof with straps wrapped around the horse’s hoof and pastern. But evidence for this improvement does not appear until the 1st century AD, long after the events in Fate’s Door.
 The actual horseshoe, nailed to the horse’s hooves, does not appear until the 5th century AD amongst the Gauls.
The actual horseshoe, nailed to the horse’s hooves, does not appear until the 5th century AD amongst the Gauls.
Although Fate’s Door is fantasy – with sea nymphs and fates as characters – my conceit is that it occurs in the 4th century BC of our world, but our world as it might have been if the ancient gods and goddesses of Greek and Norse mythology were real. So I want the historical aspects to be as close as I can make them to accurate. Which means a lot of research into things like harbor building techniques, the “Amber Road” used by traders to bring amber from the Baltic Sea to the Aegean, and hipposandals.
I find it all fascinating and hope to share more of my findings with you. 😀
For the opening to Fate’s Door, see:
Fate’s Door: The Well of Destiny
For more about Nerine’s world, see:
Knossos, Center of Minoan Culture
Measurement in Ancient Greece
Garb of the Sea People